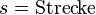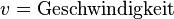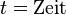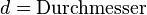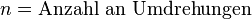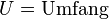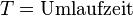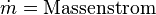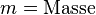Dieses Wiki, das alte(!) Projektwiki (projektwiki.zum.de)
wird demnächst gelöscht.
Bitte sichere Deine Inhalte zeitnah,
wenn Du sie weiter verwenden möchtest.
Gerne kannst Du natürlich weiterarbeiten
im neuen Projektwiki (projekte.zum.de).Gleichförmige Bewegung (konstante Geschwindigkeit): Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Aus Projektwiki - ein Wiki mit Schülern für Schüler.
MaPost (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
Belofb (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
||
| (5 dazwischenliegende Versionen von 2 Benutzern werden nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
<math>s = v * t \Longleftrightarrow v = \frac {s}{t} \Longleftrightarrow t = \frac {s}{v}</math><br /> | <math>s = v * t \Longleftrightarrow v = \frac {s}{t} \Longleftrightarrow t = \frac {s}{v}</math><br /> | ||
<math>v = \pi * d * n</math><p></p> | <math>v = \pi * d * n</math><p></p> | ||
| + | <math>U = \pi * d</math><p></p> | ||
<math>n = \frac {1}{T}</math><p></p> | <math>n = \frac {1}{T}</math><p></p> | ||
| − | <math>m = \frac {m}{t}</math><br /> | + | <math>\dot m = \frac {m}{t}</math><br /> |
| − | '''Physikalische | + | '''Physikalische Einheiten:'''<p></p> |
| − | <math>s = v * t = \frac {m*\cancel{s}}{\cancel{s}} = | + | <math>[s] = [v] *[t] = \frac {m*\cancel{s}}{\cancel{s}} = m</math><br /> |
| − | <math>v = | + | <math>[v] = \frac {m}{s}</math><p></p> |
| − | <math>t = | + | <math>[t] = s</math><p></p> |
| − | <math>n = \frac {1}{s} bzw. \frac {1}{min}</math><br /> | + | <math>[n] = \frac {1}{s} bzw. \frac {1}{min}</math><br /> |
'''Geschwindigkeitsumrechnung:'''<p></p> | '''Geschwindigkeitsumrechnung:'''<p></p> | ||
| − | <math>1 | + | <math>1 \frac {m}{s} = 3,6 \frac {km}{h}</math><p></p> |
'''Physikalische Variablen:'''<p></p> | '''Physikalische Variablen:'''<p></p> | ||
| Zeile 16: | Zeile 17: | ||
<math>v = \text{Geschwindigkeit}</math><p></p> | <math>v = \text{Geschwindigkeit}</math><p></p> | ||
<math>t = \text{Zeit}</math><p></p> | <math>t = \text{Zeit}</math><p></p> | ||
| − | + | <math>d = \text{Durchmesser}</math><p></p> | |
| + | <math>n = \text{Anzahl an Umdrehungen}</math><p></p> | ||
| + | <math>U = \text{Umfang}</math><p></p> | ||
| + | <math>T = \text{Umlaufzeit}</math><p></p> | ||
| + | <math>\dot m = \text{Massenstrom}</math><p></p> | ||
| + | <math>m = \text{Masse}</math><p></p> | ||
{{SORTIERUNG:{{SUBPAGENAME}}}} | {{SORTIERUNG:{{SUBPAGENAME}}}} | ||
| − | [[Kategorie:Techniker Schule Butzbach/Verfahrenstechnik]] | + | [[Kategorie:Techniker Schule Butzbach/Verfahrenstechnik/Physikalische Grundlagen]] |
Aktuelle Version vom 16. Januar 2019, 22:33 Uhr
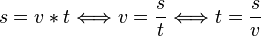
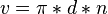
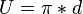
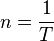
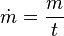
![[s] = [v] *[t] = \frac {m*\cancel{s}}{\cancel{s}} = m](/images/math/8/0/d/80d777d05a1563be3a42197f2649a0da.png)
![[v] = \frac {m}{s}](/images/math/3/7/3/3739817d9fb31dd090366de35878bb18.png)
![[t] = s](/images/math/7/2/e/72eef8729e4fd298d57a2506a1af20d0.png)
![[n] = \frac {1}{s} bzw. \frac {1}{min}](/images/math/b/b/0/bb0e100e5f2aa8907a7fef50e63bcffb.png)
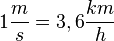 Physikalische Variablen:
Physikalische Variablen: