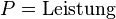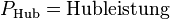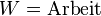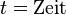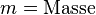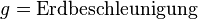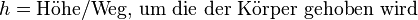Dieses Wiki, das alte(!) Projektwiki (projektwiki.zum.de)
wird demnächst gelöscht.
Bitte sichere Deine Inhalte zeitnah,
wenn Du sie weiter verwenden möchtest.
Gerne kannst Du natürlich weiterarbeiten
im neuen Projektwiki (projekte.zum.de).Leistung: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Aus Projektwiki - ein Wiki mit Schülern für Schüler.
(Kategorie:Techniker Schule Butzbach/Verfahrenstechnik/Physikalische Grundlagen) |
Belofb (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
| + | Der Begriff der Leistung, die Einheiten und Beispielaufgaben werden in diesem Video erläutert<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/sMqjKEnFoAs" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture" allowfullscreen></iframe> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Physikalische Größen und Formeln:'''<p></p> | ||
<math>P = \frac{W}{t} \Longleftrightarrow W = P * t \Longleftrightarrow t = \frac{W}{P}</math><br /> | <math>P = \frac{W}{t} \Longleftrightarrow W = P * t \Longleftrightarrow t = \frac{W}{P}</math><br /> | ||
<math>P_\text{Hub} = \frac{m * g * h}{t}</math><br /> | <math>P_\text{Hub} = \frac{m * g * h}{t}</math><br /> | ||
| − | ''' | + | '''Einheiten:'''<p></p> |
| − | <math>P = \frac{Nm}{s} = | + | <math>[P] = \frac{Nm}{s} = W</math><p></p> |
| − | <math>W = N * m = | + | <math>[W] = N * m = Nm = J</math><p></p> |
| − | <math>t = | + | <math>[t] = s</math><p></p> |
| − | <math>m = | + | <math>[m] = kg</math><p></p> |
| − | <math>g \approx 9,81 | + | <math>[g] \approx 9,81 \frac{N}{kg}</math><p></p> |
| − | <math>h = | + | <math>[h] = m</math><p></p> |
| − | ''' | + | '''Einheiten-Umrechung:'''<p></p> |
<math>1 kWh</math><p></p> | <math>1 kWh</math><p></p> | ||
<math>= 1000 Wh = 1000 W * 3600 s</math><p></p> | <math>= 1000 Wh = 1000 W * 3600 s</math><p></p> | ||
| Zeile 16: | Zeile 21: | ||
<math>= 3.600.000 J = 3600 kJ = 3,6 MJ</math><p></p> | <math>= 3.600.000 J = 3600 kJ = 3,6 MJ</math><p></p> | ||
| − | '''Physikalische | + | '''Physikalische Größen:'''<p></p> |
<math>P = \text{Leistung}</math><p></p> | <math>P = \text{Leistung}</math><p></p> | ||
<math>P_\text{Hub} = \text{Hubleistung}</math><p></p> | <math>P_\text{Hub} = \text{Hubleistung}</math><p></p> | ||
Aktuelle Version vom 28. April 2020, 10:38 Uhr
Der Begriff der Leistung, die Einheiten und Beispielaufgaben werden in diesem Video erläutert
Physikalische Größen und Formeln:
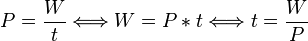
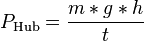
![[P] = \frac{Nm}{s} = W](/images/math/e/1/d/e1dd2143a30ba78b3693d8a5df61a02e.png)
![[W] = N * m = Nm = J](/images/math/8/f/6/8f66b558b56b527692ef5e76c88a7330.png)
![[t] = s](/images/math/7/2/e/72eef8729e4fd298d57a2506a1af20d0.png)
![[m] = kg](/images/math/d/8/0/d803f08434c7c4c94e251134caf3d4eb.png)
![[g] \approx 9,81 \frac{N}{kg}](/images/math/e/a/8/ea8bfd29e0dc5908359a39268eed6a7e.png)
![[h] = m](/images/math/f/2/c/f2c356f14dd3bdb000e9ee411c0df0c2.png) Einheiten-Umrechung:
Einheiten-Umrechung:
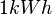
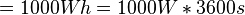
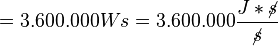
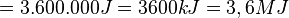 Physikalische Größen:
Physikalische Größen: